Sharks are among the ocean’s most fascinating creatures, and their eyes play an important role in their adaptations. Known for their intense appearance, shark eyes help these predators hunt and navigate effectively.
Sharks can see in low light and detect movement in deep waters, with features like a protective nictitating membrane. Understanding their eyes reveals their importance in marine ecosystems and showcases the cultural symbolism of “shark eyes” as a sign of predatory intensity. Appreciating these adaptations helps us recognize sharks’ ecological roles and the need for their conservation.
Understanding Shark Eyes
Anatomy of Shark Eyes
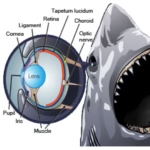
Shark eyes are intricately adapted for survival in their underwater habitats, enabling these apex predators to effectively navigate and hunt in diverse environments.
Structure
Sharks have large, well-placed eyes located on the sides of their heads, providing them with an extensive field of vision. This positioning allows them to detect movement and potential prey from various angles without needing to turn their bodies. Their eye size enhances light-gathering ability, which is especially beneficial in the dimly lit depths of the ocean. This anatomical feature is crucial for spotting prey and avoiding danger, making sharks highly efficient hunters.
Nictitating Membrane
Many shark species possess a protective layer called the nictitating membrane. This translucent membrane can cover their eyes during aggressive situations, such as when attacking prey. By shielding their eyes while still allowing for visibility, sharks protect this vital sensory organ from potential injury. This adaptation enables them to engage in predatory behavior without compromising their vision, thereby enhancing their effectiveness as hunters.
Vision Capabilities
Low-Light Vision
Shark eyes are packed with rod cells, which are specialized photoreceptors that thrive in low-light conditions. This adaptation allows sharks to see well in the dimly lit depths of the ocean, where light is scarce. With a high concentration of rod cells in their retinas, sharks can pick up even the slightest light, helping them navigate and hunt effectively during twilight or in murky waters. This ability is crucial for their survival, as many of their prey live in these dark environments, making sharks powerful hunters in their underwater realm.
Motion Detection
Furthermore, shark eyes are finely tuned to detect movement, thanks to their low-light vision. This optimization enhances their ability to locate prey even in murky or obscured conditions, allowing sharks to sense the slightest vibrations and changes in their environment. Their eyes can pick up on quick motions, such as the flapping of a distressed fish or a sudden shift in the water caused by potential prey. This keen sense of motion is crucial for hunting, as it enables sharks to react swiftly and accurately to their surroundings, significantly increasing their chances of a successful catch. Together, these visual adaptations make sharks some of the most efficient predators in the ocean.
The Meaning of “Shark Eyes”
Literal Interpretation
The term shark eyes not only captures the essence of these creatures but also pertains to the actual physical characteristics of their eyes, which contribute to their enigmatic appearance.
Coloration
Shark eyes often appear dark and reflective, especially in low-light conditions. This coloration is due to the presence of a layer called the tapetum lucidum, which enhances their ability to see in dim environments by reflecting light through the retina. This feature gives their eyes a shiny, almost luminous quality, making them stand out in the depths of the ocean. In bright light, their eyes may seem less pronounced, but in twilight or murky waters, the reflective quality becomes more apparent, adding to their mysterious allure.
Adaptation
Creating an otherworldly appearance, a shark’s gaze can change in intensity based on environmental factors. For example, when a shark is hunting or feeling threatened, its eyes may appear sharper and more intense, reflecting the predator’s heightened awareness. In contrast, when relaxed or resting, the gaze may seem softer. This adaptability serves a functional role in communication and interaction with other marine life, while also enhancing the shark’s imposing presence in the water. The shifting characteristics of their eyes contribute to the mystique surrounding sharks, evoking both fascination and fear as they glide through their underwater domain.
Metaphorical Use
In popular culture, the term shark eyes has evolved beyond its literal meaning to symbolize intensity and predatory focus, capturing the imagination of audiences across various mediums.
Movies and Literature
In films and literature, characters with sharp, piercing stares are frequently likened to sharks, evoking a sense of danger and determination. This comparison emphasizes their ability to assess situations with a keen, almost predatory awareness. For example, a character portrayed as ruthless or calculating might be described as having shark eyes, suggesting a cold, focused gaze that hints at their underlying motivations. This imagery reinforces the idea that such characters are formidable and unyielding, mirroring the relentless nature of sharks in the wild.
Everyday Sayings
In everyday language, describing someone as having “shark eyes” suggests a calm yet calculated demeanor. It implies that the person may be hiding their true intentions beneath a composed surface, indicating they are observant and perceptive. This phrase often conveys a sense of cunning or strategic thinking, as the individual might be assessing their surroundings or planning their next move, much like a shark lurking just below the surface. Such descriptions add depth to interpersonal dynamics, highlighting how a seemingly serene exterior can conceal fierce determination or intent.
Shark Behavior and Eye Function
Hunting and Feeding
Sharks rely heavily on their eyes to establish themselves as apex predators in the ocean, utilizing their exceptional vision to enhance their hunting efficiency.
Locating Prey
- Crucial Vision in Difficult Conditions: Sharks rely on their vision to spot prey even in murky waters or low light.
- Detection of Movement: Their ability to detect movement and recognize shapes allows them to locate potential meals from a distance.
- Advantageous Hunting Skills: This skill is particularly beneficial when hunting agile or camouflaged prey.
- Stealthy Stalking: The combination of acute motion detection and low-light vision enables sharks to stalk their targets stealthily, significantly increasing their chances of a successful catch.
Species Variations
- Unique Adaptations: Different shark species have evolved specific adaptations that enhance their hunting abilities.
- Hammerhead Sharks: The uniquely shaped heads of hammerhead sharks improve depth perception and expand their field of vision.
- Effective Prey Location: This anatomical feature allows them to locate prey more effectively and navigate their surroundings with greater precision.
- Diversity of Hunting Styles: Each shark species has developed adaptations tailored to its hunting style and preferred prey, showcasing the incredible diversity among these remarkable predators.
Social Interactions
Sharks also utilize their eyes in various social behaviors, which play a significant role in their interactions with one another and their environment.
Dominance Displays
Sharks also utilize their eyes in various social behaviors, which play a significant role in their interactions with one another and their environment.
Dominance Displays
- Eye Contact as a Signal: In certain shark species, maintaining direct eye contact can assert dominance within the social hierarchy.
- Avoiding Eye Contact: Sharks that avoid eye contact may demonstrate submission or a non-threatening demeanor.
- Establishing Social Order: These subtle signals help reduce aggression and maintain social structure within shark groups, allowing for more effective navigation of relationships in competitive environments.
Camouflage and Strategy
Myths and Misconceptions
Myth: Sharks Are Blind
- Highly Adapted Vision: Sharks possess excellent vision tailored to their underwater environment.
- Rod Cells: A high density of rod cells in their retinas enables them to see well in low-light conditions.
- Tapetum Lucidum: This reflective layer behind the retina enhances light detection, improving their hunting capabilities.
- Effective Predators: Their visual adaptations make sharks formidable hunters in dimly lit ocean depths.
Myth: All Sharks Have The Same Eyes
- Species Variation: Different shark species have unique eye adaptations based on their habitats.
- Hammerhead Sharks: Their distinctive head shape improves depth perception and expands the field of vision.
- Deep-Sea Sharks: These sharks have larger eyes to capture more light, aiding their survival in dark environments.
- Diversity of Adaptations: Each species showcases specific adaptations tailored to its hunting style and preferred prey, highlighting the evolutionary diversity of sharks.
Conservation and Shark Eyes
Sharks are vital for maintaining the balance and health of marine ecosystems. Their presence and behaviors significantly influence the dynamics of ocean life.
Predator Role
- Top Predators: Sharks are apex predators, meaning they sit at the top of the food chain. Their hunting activities help regulate the populations of various prey species, preventing overpopulation and maintaining species diversity.
- Control of Prey Populations: By preying on weaker or sick individuals, sharks help keep prey populations healthy. This selective pressure encourages the survival of the fittest, contributing to the overall health of marine species.
- Food Web Balance: Sharks play a vital role in the food web, influencing the distribution and behavior of other marine organisms. Their predatory habits can affect the abundance and behavior of species lower in the food chain.
Ecosystem Health
- Indicator Species: Healthy shark populations are indicators of a robust marine ecosystem. Their presence signifies a balanced environment with ample food resources and minimal pollution.
- Biodiversity Support: By regulating prey populations, sharks help maintain biodiversity. A diverse ecosystem is more resilient and better able to withstand environmental changes and stresses.
- Habitat Integrity: Sharks help sustain the integrity of various marine habitats, including coral reefs and coastal areas. Their predation can influence the behavior of herbivores, allowing for the growth and regeneration of essential marine vegetation.
Threats to Sharks
Despite their status as apex predators, sharks face a variety of serious threats that jeopardize their populations and the health of marine ecosystems.
Overfishing
- Shark Finning: The practice of shark finning involves catching sharks, removing their fins, and discarding the rest of the body at sea. This brutal practice not only reduces shark populations but also disrupts marine food webs.
- Bycatch: Sharks are often caught unintentionally in fishing gear targeting other species. This bycatch can significantly impact shark populations, particularly for vulnerable species that are already at risk.
Habitat Loss
- Pollution: Marine pollution, including plastics, chemicals, and heavy metals, affects shark health and breeding. Contaminants can accumulate in shark tissues, leading to reproductive issues and weakened immune systems.
- Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and acidification threaten shark habitats, such as coral reefs and coastal ecosystems. Changes in sea temperature can alter prey availability and migration patterns, further impacting shark populations.
- Destruction of Ecosystems: Activities such as coastal development and mangrove destruction reduce critical habitats for sharks and their prey, leading to declines in their populations.
Importance of Protection
- Preserving Unique Adaptations: Protecting sharks is essential to ensure the survival of their unique adaptations, including their specialized eyes, which are crucial for their hunting and survival strategies.
- Ecosystem Stability: By safeguarding shark populations, we help maintain the balance of marine ecosystems, which are vital for global biodiversity and the health of our oceans.
- Conservation Efforts: Implementing sustainable fishing practices, establishing marine protected areas, and raising awareness about the importance of sharks can contribute to their conservation and the preservation of marine environments.
Conclusion
Sharks are vital to the health of marine ecosystems, serving as apex predators that regulate prey populations and maintain biodiversity. Their unique adaptations, particularly their exceptional vision, play a crucial role in their hunting and survival. However, sharks face significant threats from overfishing, habitat loss, and climate change, which jeopardize their populations and the ecological balance of the oceans. Protecting sharks is essential not only for preserving their unique adaptations but also for ensuring the stability of marine environments. Conservation efforts, such as sustainable fishing practices and the establishment of marine protected areas, are critical for safeguarding these remarkable creatures and the ecosystems they inhabit.
FAQs
- What are shark eyes?
Shark eyes refer to the physical eyes of sharks, known for their intense and reflective appearance. - Why do sharks have nictitating membranes?
The nictitating membrane protects their eyes during attacks or when navigating rough environments. - Can sharks see in the dark?
Yes, sharks have excellent low-light vision due to their rod cells. - Why are shark eyes important for hunting?
Shark eyes help detect movement and locate prey even in challenging underwater conditions. - What does ‘shark eyes’ mean in popular culture?
It symbolizes an intense, predatory gaze often used to describe focus or determination. - Do all sharks have the same type of eyes?
No, different shark species have unique eye adaptations based on their habitats. - Are sharks really blind?
No, sharks have excellent vision adapted for their aquatic environments. - Why are shark eyes reflective?
The reflective quality helps sharks see in low light and murky water. - How can we help protect sharks?
Support conservation efforts, avoid shark products, and raise awareness about their ecological importance. - What role do shark eyes play in ecosystems?
Shark eyes help them hunt efficiently, maintaining balance in marine ecosystems.
If you like reading this, you may also like
Thanks for reading, for more interesting please visit our homepage.







